Speech anatomy for English pronunciation
Using a combination of anatomical diagrams and state-of-the-art 3D animations, learn how the speech anatomy is used to produce English sounds. Click on the links to watch a short video of how each sound is produced.
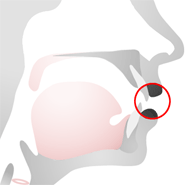
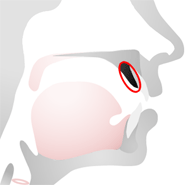
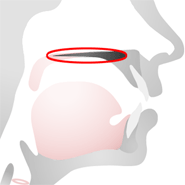
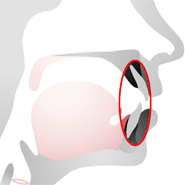
Hard Palate
The hard palate is the hard part of the roof of the mouth.
Sounds that are made with the hard palate are called palatal sounds, for example /j/.
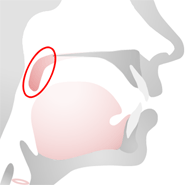
Soft Palate (velum)
The soft palate or velum is the soft portion of the roof of the mouth, lying behind the hard palate. The velum performs two important roles in speech:
- The tongue body touches the velum in order to make the sounds /k/, /g/, and /ŋ/.
- Normally during speech, the velum is in its raised position, blocking off airflow through the nose. But during some sounds (the nasal sounds, such as /m/, /n/, and /ŋ/) it lowers and allows air to flow through the nose.
Sounds that are made with the velum are called velar sounds.
Pronunciation Coach 3D
Pronunciation Coach 3D uses state-of-the-art computer animation and 3D modelling techniques to illustrate how to pronounce all of the sounds in the English language, and how to combine these sounds to pronounce any word or sentence.
Read more...
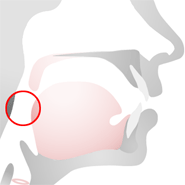
Pharynx
The pharynx is a resonating cavity or chamber lying above the larynx and posterior to the oral cavity.
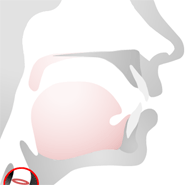
Vocal Folds
The vocal folds, also known commonly as vocal cords, are composed of twin infoldings of mucous membrane stretched horizontally across the larynx. They vibrate, modulating the flow of air being expelled from the lungs during phonation.
Sounds that are made with the vibrating vocal folds are called voiced sounds.
 Voiced
Voiced Unvoiced
Unvoiced
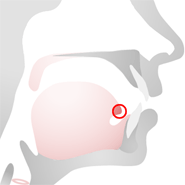
Tongue Tip (apex)
The tip of the tongue is thin and narrow, it is directed forward against the lingual surfaces of the upper incisor teeth.
Sounds that are made with the tongue tip are called apical sounds.
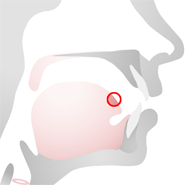
Tongue Blade
The blade is the part of the tongue lying just below the upper alveolar ridge
Sounds which are made with the tongue blade are called laminal sounds.
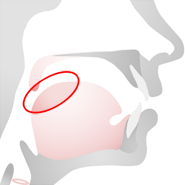
Tongue Back
The tongue back is that part of the tongue lying below the soft palate.
Sounds that are made with the tongue back are called dorsal sounds.